SEO
Monitoring SEO
Why Monitor Your Site?
Monitoring your site is important to ensure that you notice developing problems before they emerge and can take action to minimise any problems that might affect your position in search engines or the experience for your users.
There are several metrics that you could monitor - thousands, in fact - but most of us are too busy to dig into every nook and cranny and find every piece of data.
For this reason, there are several ways to combine the data you need to monitor into one central location. Google Analytics has some great resources available in the form of custom segments and dashboards, that can be shared individually or as a package.
What to Monitor
Deciding what to monitor really depends on your business or organisation and what is important to them. Ecommerce sites will have a different interest to blogging and news sites, for example.
In this series of articles we'll consider some general metrics to monitor, along with some sector-specific metrics. These articles assume that you have Google Analytics running on your website.
How to Monitor Your Site
Monitoring your website can be challenging. There are so many metrics that you need to keep an eye on, and different places you might want to gather data from.
Google Analytics allows you to embed some JavaScript code within your website that tracks the source of visits, and also the pages that the visitor passes through while they are browsing your site.
It gathers a huge amount of information including how many pages they visited, how long they spent on each page, if they dropped out of a purchase (and at which point they dropped out), how much was spent. The data is mind boggling.
This often results in being overwhelmed with the choices available, and choosing only to look at the standard 'overview' chart showing how many have visited your site in a specified time frame.
While this is useful as a start, it only scrapes the surface of the information you could analyse. The number of persons visiting your site is a 'blunt' metric. It doesn't give you an idea about how engaged they are, or what they do when they visit. It also doesn't warn you about problems that could be developing that may be masked. For example if you are starting to see a reduction in the number of 'organic' searches (searches that come from a search engine and are not via paid advertising) that might cause problems in the future.
Google appreciates the fact that the information we want to see is distributed in several places across its web-based interface, and often people do not have the time to hunt out the relevant page, filter the data, and analyse the information. Therefore, they launched some helpful features that makes it much easier to see exactly what you need with a couple of clicks every time you come into Analytics. These will be referred to throughout the monitoring section of the SEO Portal, so it's useful to become acquainted with them now.
Useful Tools
Custom Segments
Custom Segments (or Advanced Segments) provide you with the ability to chop up or segment the information in any part of Google Analytics, by filtering the data. This can be used, for example, when looking at All visits, to segment the graph into organic and paid visits, or to show how many came using 1, 2, 3 or 4+ keywords.
Custom segments are quite easy to set up. Choose which parameters you wish to use to create the filter using a drop-down select box and entering values. (If you're comfortable with regular expressions, use them.) For example, we might set up a segment:
Show me visits where keywords is equal to 2.
This would filter the data we are viewing to show all visits where two keywords were used.
The power of custom segments is huge. It allows you to selectively include and exclude data for any metric that can be used or analysed in Google Analytics.
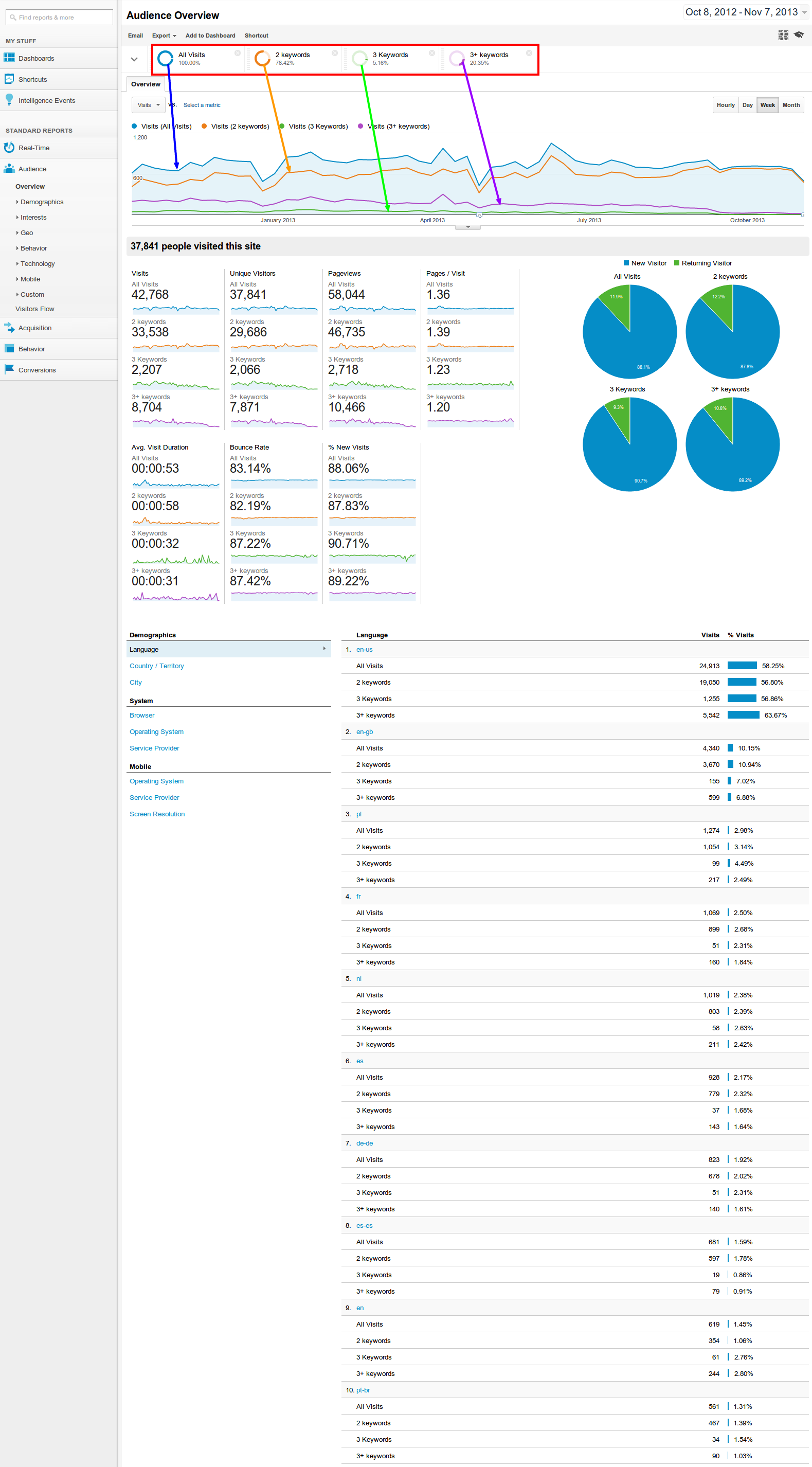
To get started with using a Custom Segment, simply click the arrow at the top of the page to display the custom segments available (outlined in red). If you have none available, you can either create your own, or import existing segments from the Google Analytics Gallery (outlined in blue).

Once you have chosen which segments you wish to use, press apply and they will be applied to the data you are viewing. Below you can see the filters being applied to show one, two, three, and three+ keywords.
Dashboards
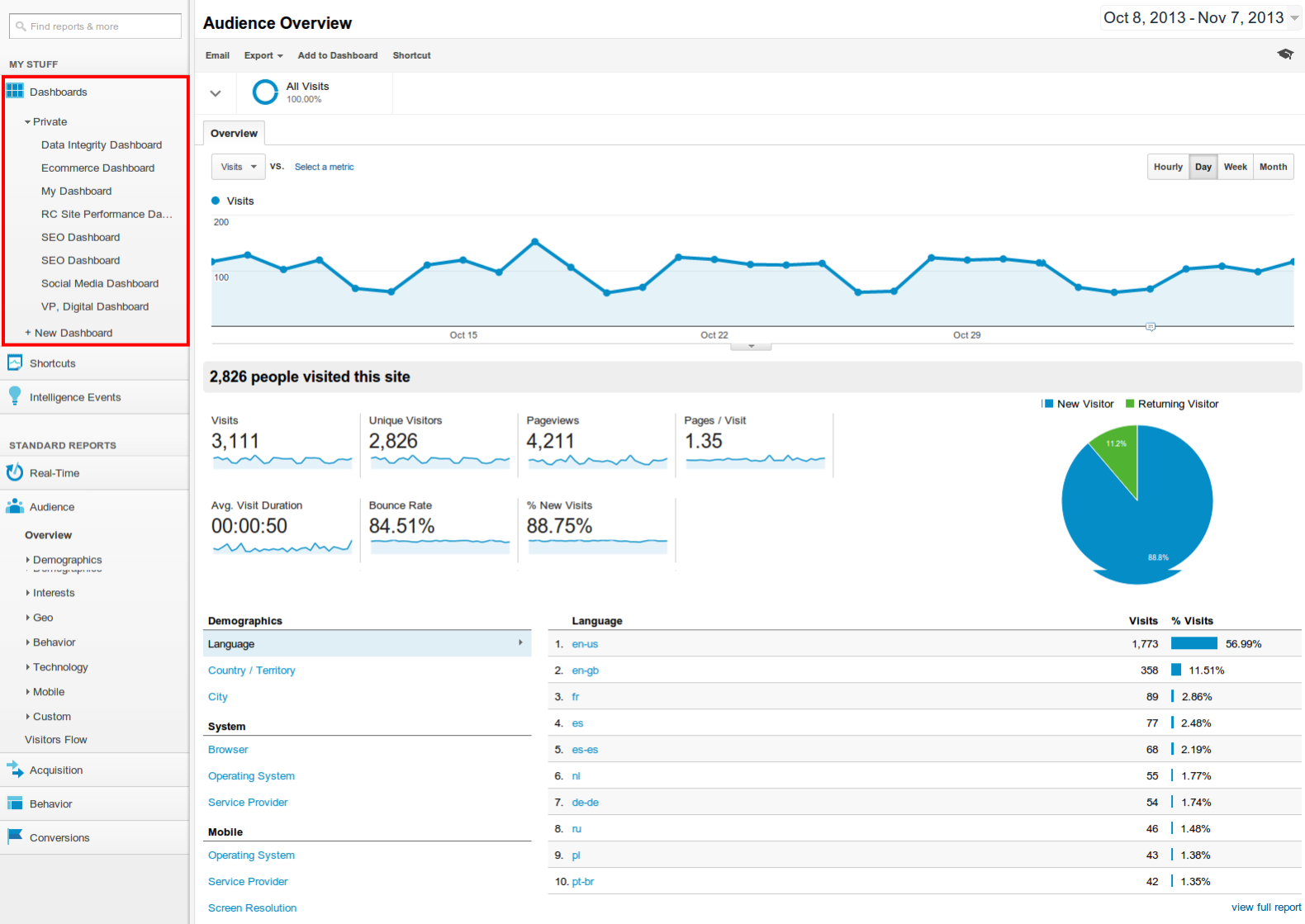
Google also rolled out a useful feature called Dashboards. This is a collection of 'widgets' in a single place, allowing you to get a quick overview of key data in one place. Before dashboards you might have to go into multiple views, run multiple filters, make sure you selected the right data. Now you can simply open the dashboard and view the data.
Dashboards can be used for any purpose and you can create (and share) your own dashboards easily with a couple of clicks.
To get started, simply expand the Dashboards section of your Analytics profile
The Google Analytics Gallery
Shortly after the Custom Segments and Dashboards were rolled out, it became evident that there was a need for a 'gallery' where people could share their segments and dashboards with others. This is a great way to get started with dashboards. You can install multiple pre-created packages that consist of segments and dashboards for specific purposes. For example, an Ecommerce bundle might include dashboards to monitor revenue, goal abandonment, mobile Ecommerce and so forth.
All you have to do is visit the gallery, choose the items you wish to install, and select the profile you wish to use.
Cyfe Dashboards
When you are managing SEO you need to have a complete view of everything going on in the business – from whether your servers are online to how many visits have been made on your social network profiles through to conversions on your website, organic traffic rates, revenue, and more.
It is often difficult to manage all this. At a basic level it means four or five tabs open and flicking between them to get an idea of what is going on.
Cyfe.com is a great tool that can be found via the Google Analytics Apps Gallery. Cyfe allows you to create dashboards and import all kinds of data from a staggering number of sources. Joomla! users can get a discount on a paid account if you mention the Documentation project.
This allows you to have multiple dashboards where you can quickly see all the metrics relating to the marketing for your website. Then you could click onto another dashboard and see the metrics relating to sales, and another to see social interaction, another to look at content.
| Monitoring for Problems | Monitoring for Performance | Monitoring for Prominence & People |
|---|---|---|
Search Engine Friendly URLs
Paths and Routes
SEF URLs make sense to both humans and search engines because they explain the path to the particular page they point to. A path is the location of a file in a directory tree or its simulation in code. Internally, the local part of a SEF URL (the part after the domain name) is called a route. Creating and processing SEF URLs is therefore referred to as routing, and the relevant code is called a router.
Search engine friendly URLs can be activated with the following steps:
- In Global Configuration
- set the Search Engine Friendly URLs option to Yes.
- Set the Use URL Rewriting option to Yes
- Optional: Set the Add Suffix to URL option to Yes.
- In the site root, rename htaccess.txt to .htaccess if you are using an Apache server, or consult the external documentation for NginX or other servers.
An example of routing can be seen in the incremental effect these changes have on the URL of the Articles Category Blog page in the sample data.
- With SEF URLs turned off in Global Configuration and .htaccess disabled, the URL is something like
https://www.example.com/index.php?option=com_content&view=category&layout=blog&id=16&Itemid=125and the breadcrumbs shows:
You are here: Home / Sample Layouts / Articles - With SEF URLs on but no URL rewriting, it becomes:
https://www.example.com/index.php/sample-layouts/articles - With both SEF URLs on, URL Rewriting on and .htaccess enabled it becomes
https://www.example.com/sample-layouts/articles.html(Add Suffix to URL set to Yes).
Numbers in non-SEF URLS
In the part of the URL that says id=16&Itemid=125 the numbers are the parameters needed to locate the internal URL and show the required page. In this case, the first numeral is the ID of a Category and the second numeral is the ID of the Category Blog menu item for that Category.
SEF URLs on Apache
Verify .htaccess is Enabled
Check that your Apache config file allows .htaccess overrides. You must make sure overrides are enabled or the .htaccess file in your Joomla! root directory will be ignored or cause an error. In the section of your virtual host configuration file or in the main (httpd.conf) configuration file you must have something similar to the example below enabling overrides:
<Directory "/home/user/public_html">
AllowOverride All
</Directory>
<Directory "/path/to/htdocs">
AllowOverride All Options=[an option],[an option],...
</Directory>
There are other ways to test if .htaccess is enabled if you do not have access to your site's configuration files. Please refer to the .htaccess tutorial found on The Apache Software Foundation website for additional information.
Step by Step
These are step-by-step instructions. Please follow them in the order they are presented here. If a step fails, do not continue until you have solved the problem.
-
Rename the file
htaccess.txtin your Joomla!'s base folder to.htaccess. -
This step may not be necessary. Open
.htaccessin a text editor. UncommentRewriteBase /(remove the first character, #). If Joomla is installed in its own folder, the enter the Joomla folder name after the forward slash. e.g.RewriteBase /yourjoomlafolder. -
Log on to your Back-end and open the Global Configuration.
-
Enable the Use Apache mod_rewrite/URL rewriting option and Save. This option uses the Apache mod_rewrite function to eliminate the "index.php" portion of the URL.
Check if your site works correctly. Your URLs should now look like:
`http://www.example.com/the-news/1-latest-news/1-welcome-to-joomla`If this option causes errors, please see How to check if mod rewrite is enabled on your server.
- If it is not enabled and you have access to the file
apache/conf/httpd.conf, open that file and check if the lineLoadModule rewrite_module modules/mod_rewrite.sois uncommented. If necessary, uncomment the line and restart the Apache web server. - If mod_rewrite cannot be enabled, leave this option off. It does not matter if you leave the
.htaccessfile renamed.
- If it is not enabled and you have access to the file
-
If you think this necessary, enable Add suffix to URLs and Save. This option adds
.htmlto the end of URLs. There are different opinions on whether this is necessary or even useful. Search engines do not seem to care if your URLs end in.htmlor not. -
Open the Plugin Manager and enable the System - SEF plugin. This plugin adds SEF support to links in your Joomla articles. It operates directly on the HTML and does not require a special tag.
SEF URLs on Nginx
Introduction
Search engine friendly (SEF), human-readable or clean URLs are URLs that make sense to both humans and search engines because they explain the path to the particular page they point to. Joomla! is capable of creating and parsing URLs in any format, including SEF URLs. This does not depend on URL rewriting executed by the web server, so it works even if Joomla! runs a server other than Apache with the mod_rewrite module. The SEF URLs follow a certain fixed pattern, but the user can define a short descriptive text (alias) for each segment of the URL.
Internally, the local part of a SEF URL (the part after the domain name) is called a route. Creating and processing SEF URLs is therefore referred to as routing, and the relevant code is called a router.
This article addresses SEF URLs under the popular, open-source Nginx web server.
Steps for NginX Servers¶
- Add the following code to your server (vhost) configuration in the nginx.conf file:
# Support Clean (aka Search Engine Friendly) URLs
location / {
try_files $uri $uri/ /index.php?$args;
}
- If the above does not work, add the following code to your server configuration in the nginx.conf file: (This worked with nginx 1.4.6 on Ubuntu.)
server {
....
location / {
expires 1d;
# Enable joomla SEF URL's inside Nginx
try_files $uri $uri/ /index.php?$args;
}
....
}
- Log on to your Backend and open the Global Configuration
- Enable the Search Engine Friendly URLs option and Save. This option converts the URLs from the native Joomla! format to the SEF format. Verify that your site works correctly. Your URLs should now look like
http://www.example.com/index.php/the-news/1-latest-news/1-welcome-to-joomla. If your site does not work correctly, please see Why does your site get messed up when you turn on SEF (Search Engine Friendly URLs)? - Enable the Use Apache mod_rewrite/URL rewriting option and Save. This option uses the Apache mod_rewrite function to eliminate the index.php portion of the URL Verify that your site works correctly. Your URLs should now look like
http://www.example.com/the-news/1-latest-news/1-welcome-to-joomla. If this option causes errors, please see How to check if mod rewrite is enabled on your server. If it is not enabled and you have access to the fileapache/conf/httpd.conf, open that file and verify that the lineLoadModule rewrite_module modules/mod_rewrite.sois uncommented. If necessary, uncomment the line and restart the Apache web server. If mod_rewrite cannot be enabled, leave this option off. It does not matter if you leave the.htaccessfile renamed. - If you think this is necessary, enable Add suffix to URLs and Save. This option adds
.htmlto the end of URLs. There are different opinions on whether this is necessary or even useful. Search engines do not seem to care if your URLs end in.htmlor not. - Open the Plugin Manager and enable the System - SEF plugin. This plugin adds SEF support to links in your Joomla articles. It operates directly on the HTML and does not require a special tag.
SEO Basics
Definition
Search Engine Optimisation is the process of improving a wide range of features of a website with the intention of improving the position in which it ranks in search engines.
The process of optimising a website is multi-faceted as there are many factors which affect where a page might rank in a search engine.
- Ensuring that content has appropriate structure using Semantic HTML
- Improving the quality of the content of individual pages.
- Ensuring that the website can handle requests quickly
- Enabling Search Engine Friendly URLs to make the web address of pages 'human readable'
- Adding contextual Semantic Markup using Schema data
Resource: Search Engine Optimization (SEO) Starter Guide
Site Structure and Descriptive URLs
In the early days, websites were structed as individual HTML files in a tree hierarchy. Some websites are still structured like that. CMSs are different. Individual pages are assembed from content stored in database tables. The URLs for the former and latter are different, perhaps like this:
https://www.example.com/user/seo/seo-basics.html
https://www.example.com/index.php?option=com_jdocmanual&view=manual&manual=user&heading=seo&filename=seo-basics
Clearly the first is easier to remember and easier to type. Search engines prefer them.
In the Joomla CMS a url of the first form can be set up as follows:
- Create a Content Category named User.
- Create a Content Category named SEO that is a child of User.
- Create an article and assign it to the SEO category.
- Create a User menu item of type of *Category List using the User category.
- Create a menu item SEO of type Category List using the SEO category.
- Set up the Joomla SEO functionality in Global Configuration.
Test it with your SEO URL: navigate via the User and SEO lists to the SEO Basics page. The Breadcrumbs should show: You are here: Home / User / SEO / SEO Basics. But not if you have created a Single Article menu item type for SEO Basics!
Reduce Duplication
The snag with CMSs is that the same content can be made available with different URLs. In the example above both URLs will work (but not on this site), as will https://example.com/index.php?option=com_content&view=category&id=18&ItemID=17. Only one of these should be recognised by search engines and set as the canonical URL. But which one and how?
The System - SEF plugin provides some help. It has three settings:
- Site Domain: If your site can be accessed through more than one domain enter the preferred (sometimes referred to as canonical) domain here. Note:
https://example.comandhttps://www.example.comare different domains. - Strict handling of index.php: This option enables a stricter handling of 'index.php' in URLs when 'Use URL Rewriting' is enabled in Global Configuration. It will remove 'index.php' if a URL still contains it and redirect incoming requests with 'index.php' to the version without the 'index.php'.
- Trailing slash for URLs: Force Joomla to only use URLs with or without trailing slash. When set, this will force the right URL with redirects and is only applied when 'Add suffix to URL' is disabled.
Canonical Tags explanation from Daniel Morell:
- How to Create Joomla Canonical Tags
- Plugin and Documentation:
For Joomla 4 and 5, before enabling, the plugin needs if ($app->isAdmin()) { changed to if ($app->isClient('admin')) { on lines 72 and 99 of plugins /system / customcanonical / customcanonical.php.
In an article, select the Publishing tab and then the Canaonical URL Auto button. This will place a link like the following any page that displays the single article:
<link href="/jdm3/en/user/seo/seo-basics.html" rel="canonical" />
Content Quality
Make what you write interesting and easy to read. Long paragraphs are often overwhelming and difficult to read. One-line paragraphs look wrong! Maybe they should really be bullet points. Aim for paragraphs of three lines or so. Read what you write and edit out any unnecesary words.
Keep your content up to date and avoid copying information from other sites. If possible, verify your content.
Semantic HTML
Content should consist of a hierarchy of headings and paragraphs with other elements as required (lists, tables and so on). Do not confuse structure with appearance - so do not use a heading for emboldment or emboldment for a heading. This is an example of semantic markup of an article:
<h2>Using headings</h2>
<p>This is an article about the importance of headings.</p>
<h2>Why use headings?</h2>
<p>It is important to use headings so that search engine bots can tell what
is an <strong>important</strong> part of your article.</p>
<h3>Types of headings</h3>
<p>You can use set types of headings, but they should be ordered, and
structured, within your page. H1 will be the page title inserted by Joomla,
with H2 being used for sub-headings of the page. Any headings within your
sub-headings should cascade using H3, H4, and H5 as appropriate.</p>
<h2>Is it hard to implement headings?</h2>
<p>It is really easy to implement headings, you just use the appropriate
HTML code.</p>
Notice that an article Title will become a <h1> heading if necessary so do not use it in an article body.
Anticipate Search Terms
Choose explicit titles for your pages and headings within pages. For example, if you don't know what Semantic HTML is or want more information on that topic those would be the words you enter into a search engine. Think of the people who might be interested in the information you are providing. What will they search for? But keep Titles and Headings fairly short - some sources say no more than 60 characters.
Care with Advertisemants
Nothing will deter site visitors more than advertisments appearing here, there and everywhere and moving the real information around before your eyes. Adverts that change every few seconds are also annoying and a drain on end-user resources. Many will use Ad-blockers!
Care with Links
Links are both a blessing and a curse! They can affect your site SEO rating for good or bad depending on whether you have links to reputable or disreputable sources. And they have to be maintained. You may have links to internal or external articles that have disappeared, present outdated information or are no longer relevant. Best advice: link if the target adds real benefit for your site visitors and use the nofollow link attribute if you do not want the target site associated with your site.
There are plenty of link checker toos available, some free or freemium and others paid, often as part of a site monitoring service.
Page Title and Description
In the <head> of every page there should be a <title> tag and a <description> tag. Joomla makes it very easy to set a different title for every page. Unfortunately, it also makes it very easy to neglect to set a suitable Title and Description on every page.
As an example, take the SEO category list page mentioned above. The page source <title> says SEO and the <description> is missing. In the Menus: Edit Item form for this menu item there is a Page Display tab with a Browser Page Title field. Insert SEO - List of Articles there and that is what appears in the <title> tag and in the browser tab.
In the Metadata tab, with the Meta Description field set to List of articles on Search Engine Optimisation. that is exactly what appears in the <description> field. The Description is sometimes used to accompany a page Title in search results so it should pay to make it relevant.
More information:
- Magazine article: Joomla SEO title tags
- Explore the Core: Native SEO Options
Optimise Images
Needless to say, attractive images can enhance a site enormously. But too many that are too large attract SEO penalties. Here are some tips:
- Place images next to the text they illustrate.
- Use descriptive alt text.
- Use minus sign separated words for the mage names for example cat-on-hot-tin-roof.jpd.
- Use the right type of image for the job: png for posters, jpg for photographs.
- Use responsive images - the is a Joomla plugin that dynamically creates webp versions of png and jpg images in several sizes.
